Example
In this example, a user has attached GSM trap actions to an SCP probe freeze detection alarm. The traps have been configured as follows:
• if an alarm goes from normal (green) to error (red), trap number 100 is sent
• if an alarm goes from error (red) to normal (green), trap number 200 is sent
In order for these traps to be successfully parsed by a third party SNMP manager, the following custom MIB entries should be added to its GSM‑MIB:
clear TRAP-TYPE
ENTERPRISE miranda
VARIABLES { trapDevice, trapAlarm }
DESCRIPTION
"A clear trap means that the alarm condition that existed has now been cleared."
::= 100
error TRAP-TYPE
ENTERPRISE miranda
VARIABLES { trapDevice, trapAlarm }
DESCRIPTION
"A error trap means that a error alarm condition is present"
::= 200
END
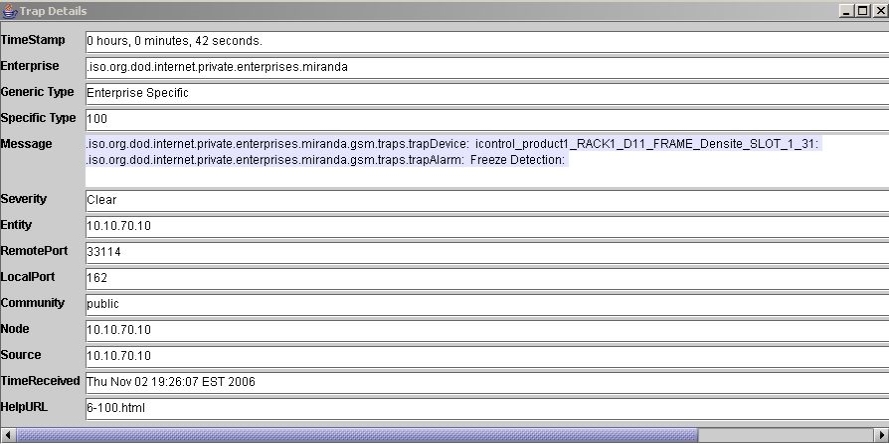
When the SCP probe freeze detection alarm goes from an error state to a normal state, a trap is sent to the specified trap target. Here’s the output of a trap catcher application.
[ Graphic ]
The trap number is shown in the Specific Type field. Variable bindings included in the trap are the trapDevice and the trapAlarm which are shown in the Message field. From the trapDevice, the SNMP manager can determine which card generated the trap. In this case it is the card with the following long ID:
icontrol_product1_RACK_D11_FRAME_Densité_SLOT_1_31
This long ID can be interpreted as follows:
[ Table ]
icontrol_product1 | Application server host name |
RACK_D11_FRAME | Densité frame name (as entered in Densité Manager) |
1 | Slot number |
9 | the slot number |
31 | the model number for the SCP-1121 card |