If multiple effects and titles has been added, real time processing may not catch up the timeline playback.
This real time processing is delayed due to the heavy data loaded on the playback operation. While playback is performed, the lines of the parts where rendering is required are displayed in red (overloaded) or in orange (loaded).
Performing rendering enables smoother playback.
Realtime processing sometimes cannot keep up when playing back a timeline. The line of the part judged as requiring rendering when playing back changes color.
The line colors indicate the following states.

|
Line color |
Timeline state |
|---|---|
|
No line |
No clip exists. |
|
Blue |
A clip matching the project settings is placed. |
|
Light blue |
Playback is keeping up. (Rendering is sometimes required.) |
|
Orange |
Rendering option (load area) |
|
Red |
Rendering is required (overload area). |
|
Green |
Already rendered |

Rendering is judged based on the remaining buffer set by [Application] in [System Settings] → [Render], and a red line is displayed for overload areas when the remaining buffer is less than the preset value.
When data such as CG animation has been placed one frame at a time as consecutive still images on the timeline, rendering the area will not lighten the load of playback processing. In this case, use the [Render and Add to Timeline (Between In/Out)] function to replace with the exported clip.
Rendering is enabled even if the clip becomes out-of-position by a ripple delete, for example.
|
|
|---|
|
Render all the areas that are judged as overload (red) in the entire sequence.
1) Click the [Render In/Out (Render Overload Area)] list button on the timeline.
2) Click [Render Sequence] → [Render Overload Area].
To cancel rendering, click [Cancel] in the [Render] dialog box.
Lines in the rendered areas on the time scale change color to green.
 Alternative
Alternative
Click [Render] on the menu bar, and click [Render Sequence] → [Render Red Area].
Rendering overload areas on the entire sequence: [Shift] + [Ctrl] + [Q]

Overload (red) and load (orange) areas on the entire sequence can be rendered at a time by the following operation.
Click the [Render In/Out (Render Overload Area)] list button, and click [Render All] → [Render Loaded Area].
Click [Render] on the menu bar, and click [Render Sequence] → [Render Orange Area].
Rendering (load areas) on the entire sequence: [Shift] + [Ctrl] + [Alt] + [Q]
When the In and Out points are set on the timeline, only the range between In and Out points is rendered.
Render all areas that are judged as overload (red) in the entire project that comprises multiple sequences.
1) Click [Render] on the menu bar, and click [Render Entire Project] → [Render Red Area].
To cancel rendering, click [Cancel] in the [Render] dialog box.
Lines in the rendered areas on the time scale change color to green.

Overload (red) and load (yellow) areas in the entire project can be rendered at a time. Click [Render] on the menu bar, and click [Render Entire Project] → [Render Orange Area].
Render only the areas that are judged as overload (red) or load (orange).
1) Right-click the line of overload (red) or load (orange) areas on the time scale, and click [Render].
To cancel rendering, click [Cancel] in the [Render] dialog box.
Lines in the rendered areas on the time scale change color to green.
Render areas judged as overload (red) between In and Out points on the timeline.
1) Setting the In and Out Points to the Timeline
2) Click [Render In/Out (Render Overload Area)] on the timeline.
To cancel rendering, click [Cancel] in the [Render] dialog box.
Lines in the rendered areas on the time scale change color to green.
 Alternative
Alternative
Click [Render] on the menu bar, and click [Render In/Out] → [Render Red Area].
Click the [Render In/Out (Render Overload Area)] list button, and click [Render In/Out] → [Render Overload Area].
Right-click the time scale, and click [Render In/Out] → [Render Overload Area].
Rendering overload areas between In and Out points: [Ctrl] + [Q]

All areas judged to be red, orange and light blue between In and Out points can be rendered by the following operation.
Click [Render] on the menu bar, and click [Render In/Out] → [All].
Click the [Render In/Out] list button, and click [Render In/Out] → [All].
Right-click the time scale, and click [Render In/Out] → [All].
Rendering between In and Out points (all): [Shift] + [Alt] + [Q]
Overload (red) and load (orange) areas between In and Out points can be rendered at a time by the following operation.
Click [Render] on the menu bar, and click [Render In/Out] → [Render Orange Area].
Click the [Render In/Out (Render Overload Area)] list button, and click [Render In/Out] → [Render Loaded Area].
Right-click the time scale, and click [Render In/Out] → [Render Loaded Area].
Rendering between In and Out points (load area): [Ctrl] + [Alt] + [Q]
Render only overload areas (red) or load areas (orange) around the timeline cursor position.
1) Move the timeline cursor to the area to be rendered.
2) Click [Render] on the menu bar, and click [Render Cursor Area].
To cancel rendering, click [Cancel] in the [Render] dialog box.
Areas of the same line color on the time scale are rendered around the timeline cursor position. When there is a transition in same-color lines, the rendered area becomes the area up to the In or Out point of the transition.
Lines in the rendered areas on the time scale change color to green.
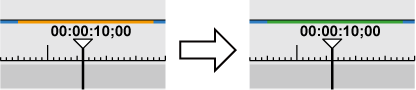
Perform rendering in individual clip or transition units.
|
|
|---|
|
1) Right-click the clip to be rendered, and click [Render].
To render a transition, right-click the transition and click [Render].
To cancel rendering, click [Cancel] in the [Render] dialog box.
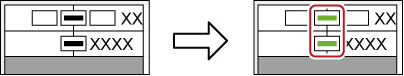
When rendering is completed, a green line is displayed on the clip.
When a clip has been rendered
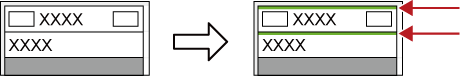
When a transition has been rendered, the center line of the transition changes color to green.
When a clip transition has been rendered
 Alternative
Alternative
Click [Render] on the menu bar, and click [Render selected clip/transitions].
Rendering clips/transitions: [Shift] + [G]
Render between In and Out points on the timeline, and export only video clips as a file in AVI format. Exported clips are placed on the V/VA track.
1) Set the area of the clip to export from the timeline with the In and Out points.
2) Click the [Render In/Out (Render Overload Area)] list button on the timeline.

3) Click [Render and Add to Timeline (Between In/Out)].
To cancel export, click [Cancel] in the [Render] dialog box.
When rendering is completed, the video clip which has been exported to the V/VA track of the timeline is placed.
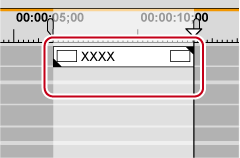
If there is no space to place a clip on the track, a new V track is added.
 Alternative
Alternative
Click [Render] on the menu bar, and click [Render and Add to Timeline (Between In/Out)].
Right-click the time scale, and click [Render and Add to Timeline (Between In/Out)].
Exporting video clips from the timeline: [Shift] + [Q]

Exported clips are saved in the “rendered” folder in the project folder.
|
|
|---|
|
Video images in the selected preview window (Player/Recorder) can be exported as still image clips and registered to the bin.
To export the frame displayed on the Recorder as a still image
1) On the Recorder, display frames to be saved as still images.
2) Click [Create a Still Image (Save as)] on the timeline.
The [Save As] dialog box appears.
3) Set a file name, save destination, and [Save as type], and then click [Save].
The still image is saved in the specified folder, and the still image clip is registered to the bin.
 Alternative
Alternative
Exporting still image clips from the timeline: [Ctrl] + [T]
Click [Clip] on the menu bar, and click [Create a Still Image]. The still image is saved in the same folder as the project, and the still image clip is registered to the bin.

Still images are saved as side-by-side in the stereoscopic edit mode.
Video from a deck also can be saved as still image clips.
The aspect ratio of still images sometimes is output different from that of the original image depending on the frame size. To output correctly, set to correct the aspect ratio. The settings of still images to export can be changed by [Importer/Exporter] in [System Settings] → [Still Image].
Manually delete temporary files that are created during rendering.
Temporary files for rendering are saved temporarily in the “rendered” folder created in the project folder. Temporary files that are not referenced by a project are automatically deleted when the project ends, however, it is recommended to manually delete them when the “rendered” folder increases in size.
1) Click the [Render In/Out (Render Overload Area)] list button on the timeline.

2) Select [Delete Render Files] and click [Files that are not Used] or [All Files].
 Alternative
Alternative
Click [Render] on the menu bar, and click [Delete Temporary Render Files] → [Files Not Used] or [All Files].
Deleting unused files: [Alt] + [Q]
3) Click [Yes].

Set when to automatically delete invalid rendering files (i.e. files not referenced by a project) at [Application] in [System Settings] → [Render].
A temporary file is created in the following cases:
When a clip has been exported from the timeline
When part of the timeline has been rendered
When a clip has been rendered
|
|
|---|
|
Reducing image resolution or bit depth for preview improves the performance of real time playback. Although the preview image quality becomes lower, it reduces the load on PC and you can edit data comfortably.
Make use of this feature when you apply heavy-load effects such as [Mask] and [Layouter], or when you play the timeline where high-resolution clips such as 4K are placed.
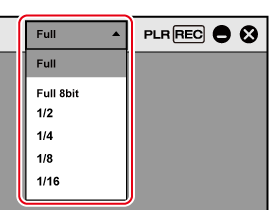
1) Click [Preview Quality] on the menu bar, and select an item.
The image quality of the preview window will be changed according to the selected item.
|
[Full] |
Previews video without changing the resolution and bit depth. |
|
[Full 8bit] |
Previews video with the original resolution maintained but with the bit depth changed to 8 -bit. This is displayed only for projects with video quantization bitrate of 10 -bit. |
|
[1/2] |
Previews video in 1/2 of the original resolution. |
|
[1/4] |
Previews video in 1/4 of the original resolution. |
|
[1/8] |
Previews video in 1/8 of the original resolution. |
|
[1/16] |
Previews video in 1/16 of the original resolution. |

Click [Settings] on the menu bar, go through [User Settings] → [Preview] → [Playback], and add the check mark for [Show full quality when Paused], to enable preview in the original image quality when playback is paused.
When proxy editing is started while [Preview Quality] is set to [Full] or [Full 8bit], the setting is automatically changed to [1/2]. When proxy editing is started while [Preview Quality] is set to lower than [1/2], the setting is maintained. After proxy editing is finished, [Full] is applied for [Preview Quality], regardless of the original setting.
|
|
|---|
|
When heavy-load effects such as [Mask] or [Layouter] are applied on a clip, real time processing may not catch up and the timeline may not be played back smoothly.
Draft preview can be used in such a case. Although the preview image quality becomes lower, it does not take time for converting resolution or bit depth, and the timeline can be played back quickly. If you need to check image details, adding the check mark for [Show full quality when Paused] can let you check the image in the original quality when playback is paused.
Changing Image Quality for Preview
Draft preview is effective in playback of timeline where the data amount is large due to a case such as heavy usage of high quality 4K image clips.
For example, when [1/2] is selected for [Preview Quality], 4K (3840x2160) video is displayed in the image quality equivalent to Full HD (1920x1080). If you edit video on a notebook PC, selecting [1/4] and previewing in full screen can maintain an adequate image quality.
By using the draft preview, you can handle high-quality image sources regardless of the performance of your PC.
Draft preview functions effectively in the following formats.
Sony RAW, Cinema RAW, Cinema RAW Light, Avid DNxHD/Avid DNxHR, Apple ProRes, RED, Motion JPEG, JPEG, Grass Valley HQX