When starting up EDIUS, you can create projects with different settings from that set in detail as a project preset (rendering formats, track numbers, etc.)
|
|
|---|
|
1) Enter a project file name in [Project name] of [Project file] in the [Project Settings] (Simple Settings) dialog box.
2) Select a project preset.
3) Check [Customize], and click [OK].
The [Project Settings] (Detailed Settings) dialog box appears.
4) Configure a project, and click [OK].
|
[Video Preset] |
Display a list of commonly used video formats. From this list, select a video format that suits the export environment. |
|
[Audio Preset] |
Display a list of commonly used audio formats. From this list, select an audio format that suits the export environment. |
|
|
Click this button for detailed settings. |
|
[Advanced] |
Click the expand button to customize detailed settings based on the format selected in [Video Preset] and [Audio Preset]. You cannot change the items displayed in gray. [Frame Size] Select a frame size from the list. Select [Custom] to enter a setting value in pixel. (The width must be a multiple number of 4. The maximum value is 4096x2160 pixel.) [Aspect Ratio] Select an aspect ratio from the list. [Frame Rate] Select a frame rate from the list. [Field Order] For interlace, a field order can be selected. [Video Channel] Select the channel to be exported (color channel/alpha channel) from the list. Select [YCbCr] to export only color channel. Select [YCbCr + Alpha] to export both color channel and alpha channel. [Video Bit Depth] Select a video quantization bitrate from the list. [Pulldown Type] This setting is only available for a frame rate of 24p or 23.98p. Select a convert format to convert a 23.98p video to a 59.94i or 59.94p video signal. [Pulldown(2-3-2-3)] enables a smooth playback, but is not appropriate for re-editing. Select this item for the final export. [Advanced pulldown(2-3-3-2)] does not provide a smooth playback. Select this item to create a temporary file to edit. [Color Space] Select the color space of the project. [Stereoscopic Editing] For 3D editing, select [Enable]. The stereoscopic edit mode is set. [Sampling Rate] Select an audio sampling rate from the list. [Audio channel] Select the number of audio channels from the list. [Audio Bit Depth] Select an audio quantization bitrate from the list. |
|
[Setup] |
[Render format] Select the default codec to be used for rendering and file export during editing. RGB, UYVY, YUY2, RGBA and v210 are uncompressed AVI. For some codec, the rendering quality can be configured by clicking [Detail]. [Overscan Size] Enter the ratio when you use overscan. The value range is between “0” and “20”. If you do not use overscan, enter “0”. [Audio reference level] Set the audio reference level. If you switch the display of the [Audio Mixer] dialog box to a VU meter, a scale with the specified audio reference level at “0” is displayed. [Resampling method] Select a resampling method when transforming video with the layouter. [HDR/SDR gain] Set the gain value to be applied when the color space of either HDR or SDR is converted to/from the other. In some conditions, the brightness of the reference white of HDR may differ from that of SDR. In this case, a video converted from HDR to SDR will appear brighter, and that converted from SDR to HDR will appear darker. Setting [HDR/SDR gain] will apply the gain value when the color space of either HDR or SDR is converted to/from the other, preventing the variation in brightness. Set the gain value to the conversion value for the display light. Select an item from [Disable], [0.00 dB], [3.00 dB], [6.00 dB], [6.15 dB], [9.00 dB] and [12.00 dB]. Select [6.15 dB] to comply with ITU-R BT.2408. You can also directly enter a value (unit: dB) within a range from “0.00” to “20.00”.
[Tone mapping] This setting is applied to conversion in which the dynamic range of the color space gets smaller, such as when a HDR source is used as SDR. Setting [Disable] will not apply the tone mapping. Areas with brightness that exceeds the luminance range of SDR will be replaced to 100% white. Setting [Soft Clip] will compress the high-luminance areas to show smooth gradation so that they will not be clipped easily.
|
|
[Sequence setup (Default)] |
Default settings for creating a sequence. [TC preset] Enter the start timecode of the timeline. [TC Mode] When NTSC has been selected for the project setting, select either drop frame or non drop frame timecode display. [Total length] Set the length of the timeline by entering a number when the final total length is fixed. When the project exceeds this length, the color of the timeline section that is over the limit change. |
|
[Track (Default)] |
Default settings of a number of tracks and a channel map for creating new projects or sequence. [V Tracks]/[VA Tracks]/[T Tracks]/[A Tracks] Set the number of tracks in which you place clips. You can add or delete any tracks after opening a project. [Channel map] In the [Audio Channel Map] dialog box, configure the audio output channel of each track. |

Formats that can be exported with alpha channel retained when [Video Channel] is set to [YCbCr + Alpha] are as follows.
Grass Valley HQ AVI
Grass Valley HQ QuickTime
Grass Valley HQX AVI
Grass Valley HQX QuickTime
Uncompressed RGBA AVI
ProRes 4444 MOV
To create a project in a format with resolution of other than 4K or video format (such as resolution for square shape), select the following codec for [Render format] in [Setup].
[Grass Valley HQX SuperFine]
[Grass Valley HQX Fine]
[Grass Valley HQX Standard]
[Grass Valley HQX Offline]
|
|
|---|
|
You can configure the rendering quality for each codec in the [Project Settings] (Detailed Settings) dialog box.
[Project Settings] (Detailed Settings) Dialog Box
For the details of the items, see the [Settings - Grass Valley HQ]/[Settings - Grass Valley HQX] dialog box of [Preset Wizard], by clicking [Hardware] in [System Settings] → [Device Preset]. Click [Save as default] to save the current settings as defaults.
[Settings - Grass Valley HQ]/[Settings - Grass Valley HQX] Dialog Box
|
[Segment Encode] |
Check this item to export a clip of a raw source without re-encoding. Output speed is fast. |
|
[Size] |
Select an image quality. |
|
[Quality/Speed] |
Select quality from the list. The higher the quality, the more time it takes to be encoded. |
|
[Bit Rate] |
Select a bitrate type. [CBR] sets a fixed transfer rate, allocating a fixed number of bits during the encoding process. Select a bitrate from the [Average(bps)] list. You can also enter a value directly. [VBR] sets a variable transfer rate, altering the number of assigned bits according to the complexity of the movement or image quality. Compared with [CBR], the media volume can be used more efficiently, and this enables more consistent image quality overall. Select a bitrate from the [Average(bps)] and [Maximum(bps)] lists. You can also enter a value directly. |
|
[Field Order] |
For interlace, a field order can be selected. |
|
[Chroma Format] |
Select a YUV pixel format from the list. |
|
[Profile & Level] |
Select a profile & level. If [Chroma Format] is [4:2:0] and [4:2:2], the profile will be set to Main Profile and 422Profile, respectively. The level for SD image quality will be Main Level, and the level for HD image quality will be High Level. The profile & level changes according to the format selected in [Chroma Format]. |
|
[GOP Structure] |
For MPEG, a certain number of frames is considered as a group, and operations such as compression/enlargement and cut editing are performed on a GOP basis. A GOP comprises “I frame”, “P frame” and “B frame”. The I frame allows images to be reproduced independently, the P frame is for recording and reproducing only the differences with the preceding image, and the B frame reproduces images from the differences in the preceding and following images. Select I, P and B frame patterns of the GOP from the list. Normally, select [IBBP]. [I-Frame Only] is comprised of only I-pictures. Editing is made easier, but the amount of data increases in size. |
|
[Picture count] |
Set the number of frames included in a group. |
|
[Closed GOP] |
Check this item to complete information within each GOP. Although the amount of data increases, the video can be re-edited using software that supports GOP-based editing. Normally, leave this item unchecked. |
|
[Emphasis] |
Select an item from the list for high-frequency compensation that saves while emphasizing the high range. [None] is a setting without high-frequency compensation. [50/15 us] is an emphasis setting employed by some audio CDs, etc. [CCITT J.17] is a telecommunications standard recommended by CCITT. |
|
[Protection] |
The “protection_bit” indicates whether redundancy is added to an audio bit stream in order to make error detection and correction possible. Check this item to change it to “1”, indicating that redundancy is being added. Uncheck this item to change it to “0”, indicating that redundancy is not being added. |
|
[Original Flag] |
Check this item to change the “original_copy” bit to “1”, indicating the original copy. If it is unchecked, it becomes “0”, indicating a duplication. |
|
[Copyright Flag] |
Check this item to change the “copyright” bit to “1”, indicating that the copyright is protected. If it is unchecked, it becomes “0”, indicating there is no copyright. |
Items that can be configured are the same as [MPEG2 Program Stream].
|
[Segment Encode] |
Check this item to export a clip of a raw source without re-encoding. This increases the output speed. |
|
[Bit Rate] |
Select a bitrate type. [CBR] sets a fixed transfer rate, allocating a fixed number of bits during the encoding process. Select a bitrate from the [Average] list. You can also enter a value directly. [VBR] sets a variable transfer rate, altering the number of assigned bits according to the complexity of the movement or image quality. Compared with [CBR], the media volume can be used more efficiently, and this enables more consistent image quality overall. Select a bitrate from the [Average] and [Max] lists. You can also enter a value directly. |
|
[Quality/Speed] |
Select quality from the list. The higher the quality, the more time it takes to be encoded. |
|
[Field Order] |
For interlace, a field order can be selected. |
|
[GOP Structure] |
For MPEG, a certain number of frames is considered as a group, and operations such as compression/enlargement and cut editing are performed on a GOP basis. A GOP comprises “I frame”, “P frame” and “B frame”; the I frame allows images to be reproduced independently, the P frame is for recording and reproducing only the differences with the preceding image, and the B frame reproduces images from the differences in the preceding and following images. Select I, P and B frame patterns of the GOP from the list. Normally, select [IBBP]. [I-Frame Only] is comprised of only I-pictures. Editing is made easier, but the amount of data increases in size. |
|
[Picture count] |
Set the number of frames included in a group. |
|
[Closed GOP] |
Check this item to complete information within each GOP. Although the amount of data increases, the video can be re-edited using software that supports GOP-based editing. Normally, leave this item unchecked. |
|
[Chroma Format] |
Select a YUV pixel format from the list. |
|
[Profile/Level] |
Select a profile & level. If [Chroma Format] is [4:2:0] and [4:2:2], the profile will be set to Main Profile and 422Profile, respectively. The level for SD image quality will be Main Level, and the level for HD image quality will be High Level. The profile & level changes according to the format selected in [Chroma Format]. |
|
[Format] |
Select a format from the list. |
|
[Format] |
Select a format from the list. |
|
[Quality/Speed] |
Select quality from the list. The higher the quality, the more time it takes to be encoded. |
|
[ClosedGOP] |
Check this item to complete information within each GOP. Although the amount of data increases, the video can be re-edited using software that supports GOP-based editing. |
|
[Segment Encode] |
Check this item to export a clip of a raw source without re-encoding. This increases the output speed. |
|
[Bit Rate] |
Select a bitrate from the list. |
|
[Segment Encode] |
Check this item to export a clip of a raw source without re-encoding. Output speed is fast. If the frame rate of the export format is 23.98p, segment encode is not available. [Quality/Speed] Select the quality of the part to be re-encoded from the list. The higher the quality, the more time it takes to be encoded. |
Check [Use MSDV codec] to export the content to an MSDV codec AVI.
The following codecs can also be selected.
[Detail] will not be available.
AVCIntra MXF
DVCPROHD MXF
DVCPRO25 MXF
DVCPRO50 MXF
DV MXF
Uncompressed RGB AVI
Uncompressed RGBA AVI
Uncompressed UYVY AVI
Uncompressed YUY2 AVI
Uncompressed v210 AVI
Grass Valley Lossless AVI
DVCPRO50 AVI
Select the final output channel for the output from the track.
1) Click [Channel map] in the [Project Settings] (Detailed Settings) dialog box.
The [Audio Channel Map] dialog box appears.
2) Click the point where the track and the channel to output intersect to configure the audio channel map.
Every click switches between [Stereo], [Mono], and [No Output folder].
For stereo output, use a combination of an odd number channel and an even number channel and set this option to [Stereo]. If you output in monaural, select [Mono], and if you do not output anything, select [No Output folder]. If the setting is invalid, “-” is displayed.
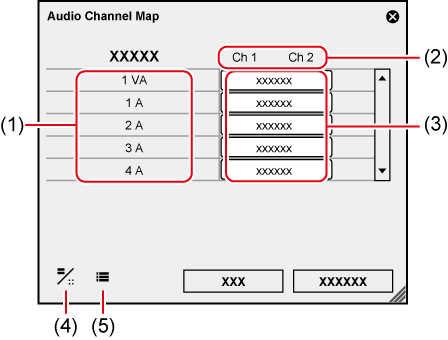
|
(1) |
Tracks |
The number or type of track to be displayed differs depending on the [Track (Default)] settings in the project settings. |
|
(2) |
Output channels |
The number of channels to be displayed differs depending on the [Audio Preset] or [Audio Channels] settings in the project settings. |
|
(3) |
Audio channel map settings |
Select the output channel for the output from the track. Every click switches between [Stereo], [Mono], and [No Output folder]. |
|
(4) |
[Change Display Style] |
Click this item to switch the display view of the [Audio Channel Map] dialog box. |
|
(5) |
[Preset] |
Register the settings as a preset. |

Use the track header to place an audio channel of the source clip to a desired track.
|
|
|---|
|
You can register frequently used audio channel map settings as presets.
1) Configure the audio channel map in the [Audio Channel Map] dialog box.
2) Click [Preset], and click [Save].
3) Enter a preset name, and click [OK].

You can overwrite an existing audio channel map preset with the current settings. In step 2) , click [Preset], and click [Update] → [Preset Name]. Confirm the preset name, and click [OK].
To display a list of the audio channel map presets, click [Preset] in the [Audio Channel Map] dialog box, and click [Properties].
Switch the audio channel map presets to use.
1) Click [Preset] in the [Audio Channel Map] dialog box, and click [Load].
A list of the audio channel map presets is displayed.
2) Select a preset, and click [OK].
You can delete audio channel map presets you created.
1) Click [Preset] in the [Audio Channel Map] dialog box, and click [Properties].
A list of the audio channel map presets is displayed.
2) Select a preset, and click [Delete].
3) Click [Yes].
Import an audio channel map preset.
1) Click [Preset] in the [Audio Channel Map] dialog box, and click [Properties].
A list of the audio channel map presets is displayed.
2) Click [Import].
3) Select a file, and click [Open].
Export an audio channel map preset you created.
1) Click [Preset] in the [Audio Channel Map] dialog box, and click [Properties].
A list of the audio channel map presets is displayed.
2) Select a preset, and click [Export].
The [Save As] dialog box appears.
3) Set a file name and save destination, and click [Save].